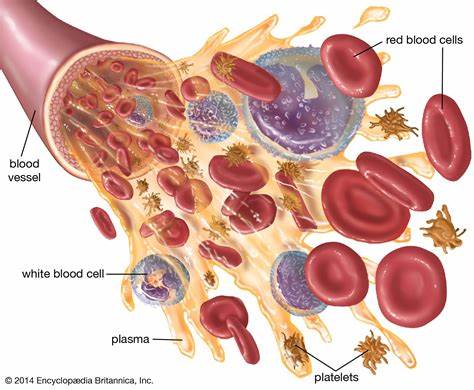
The components of
blood include plasma, platelets, and red and white blood cells
that circulate through the body. Blood supplies essential substances, such as sugars and oxygen, to cells and
organs, and removes waste from cells.
The main components of blood are:
Plasma accounts for around 55% of blood fluid in
humans. Plasma is 92% water, and the contents of the remaining
8% include:
→ glucose
→ hormones
→ proteins
→ mineral salts
→ fats
→ vitamins
The remaining 45% of blood mainly consists of red and white blood cells and platelets. Each of these has a vital
role to play in keeping the blood functioning effectively.
Red blood cells have a slightly indented, flattened disk shape. They transport oxygen to and from the lungs. Hemoglobin is a protein that contains iron and carries oxygen to its destination. The life span of a red blood cell is 4 months, and the body replaces them regularly. The human body produces around 2 millionTrusted Source blood cells every second. The expected number of red blood cells in a single drop (microliter) of blood is 4.5–6.2 million in males and 4.0–5.2 million in females.
White blood cells make up less than 1% of blood content, forming vital defenses against disease and infection. The number of white blood cells in a microliter of blood usually ranges from 3,700–10,500. Higher or lower levels of white blood cells can indicate disease.
Platelets interact with clotting proteins to prevent or stop bleeding. There should be between 150,000 and 400,000 platelets per microliter of blood. Bone marrow produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, and from there they enter the bloodstream. Plasma is mostly water that is absorbed from ingested food and fluid by the intestines. The heart pumps them around the body as blood by way of the blood vessels.
Blood has
various functions that are central to survival. They include:
→ supplying oxygen to cells and tissues
→ providing essential nutrients to cells, such as amino acids, fatty acids, and glucose
→ removing waste materials, such as carbon dioxide, urea, and lactic acid
→ protecting the body from diseases, infections, and foreign bodies through the action of white
blood cells
→ regulating body temperature
→ Blood plays a large role in digestion and endocrine system functions. Digested nutrients are
absorbed into the bloodstream through capillaries in the villi that line the small intestine. These nutrients
include glucose, amino acids, vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids.
Blood also transports some hormones secreted by endocrine system glands to target organs and tissues.
The platelets in blood enable the clotting, or coagulation, of blood. When bleeding occurs, the platelets group
together to create a clot.
The clot forms a scab, which stops the bleeding and helps protect the wound from infection..
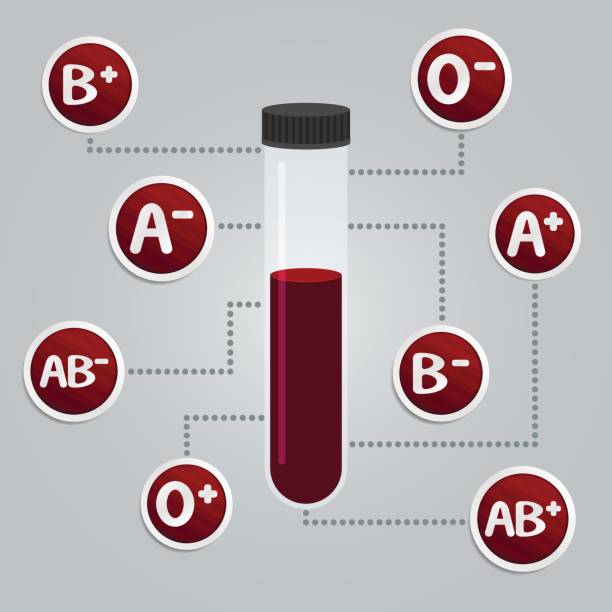
A person’s
blood type is determined by the antigens on the red blood cells. Antigens are protein molecules on the surface
of these cells.
Antibodies are proteins in plasma that alert the immune system to the presence of potentially harmful foreign
substances. The immune system protects the body from the threat of disease or infection.
Knowing a person’s blood type is essential if they are receiving an organ donation or blood transfusion.
Antibodies will attack new blood cells if the blood is the wrong type, leading to life threatening
complications.
For example, anti-A antibodies will attack cells that have A antigens.
Red blood cells sometimes contain another antigen called RhD. Doctors also note this as part of the blood group.
A positive blood group means that RhD is present.
Humans can have one of four main blood groups. Each of these groups can be Rhd-positive or -negative, forming
eight main categories.
Group A positive or A negative:A antigens are present on the surfaces of blood cells. Anti-B antibodies are present in the plasma.
Group B positive or B negative:B antigens are present on the surfaces of blood cells. Anti-A antibodies are present in the plasma.
Group AB positive or AB negative:A and B antigens are present on the surfaces of blood cells. There are no antibodies in the plasma.
Group O positive or O negative:There are no antigens on the surfaces of blood cells. Both anti-B and anti-A antibodies are present in the plasma.
Disorders and
diseases of the blood can
impair the many functions that blood performs.
Some common blood disorders are:
Anemia:This happens when low red blood cell or hemoglobin levelsTrusted Source mean the cells do not transport oxygen effectively, leading to fatigue, pale skin, and other symptoms.
Blood clotting:Clotting helps wounds and injuries heal, but blood clots that form inside a blood vessel can create a blockage, which can be life threatening. If clots become dislodged and move through the heart to the lungs, a pulmonary embolism can form.
Blood cancers:Cancers such as leukemia, myeloma, and lymphoma occur when blood cells start to divide uncontrollably without dying off at the end of their life cycle.
Hemophilia:If a person has low levels of clotting factors in the blood, they can bruise or bleedTrusted Source very easily. They may bleed for too long after a minor injury or surgery, or during menstruation. It affects around 18,000 peopleTrusted Source in the U.S.
Thalassemia: This is also a type of inherited anemia in which the body produces an unusual form of hemoglobin. It affected around 1,000Trusted Source people in the U.S. in 2008 and is most common in people from around the Mediterranean and parts of Asia. If symptoms suggest a person may have a blood disorder, they should seek medical advice. A doctor may refer them to a specialist in blood disorders, known as a hematologist.
Donating blood can help people
with many health conditions, such as those who:
→ have internal or external bleeding due to an injury
→ have sickle cell disease or another illness that affects the blood
→ are undergoing surgery, such as cardiovascular or orthopedic surgery
→ have an inherited blood disorder
→ need treatments involving plasma or other blood products
→ are undergoing a transplant
The remaining 45% of blood mainly consists of red and white blood cells and platelets. Each of these has a vital
role to play in keeping the blood functioning effectively.
Donating blood is safe, as long as the center follows the standard guidelines.The U.S. and many other countries have strict regulations to ensure safety. The FDA and American Association
of Blood Banks (AABB) monitor blood banks for this purpose.
Safety precautions they take include:
→ screening donors for existing health conditions
→ using new needles for each donation
→ having professional staff on hand
→ providing monitoring and refreshments to ensure a safe recovery